The Evolution of Laser Alignment: From Basic to Brilliant
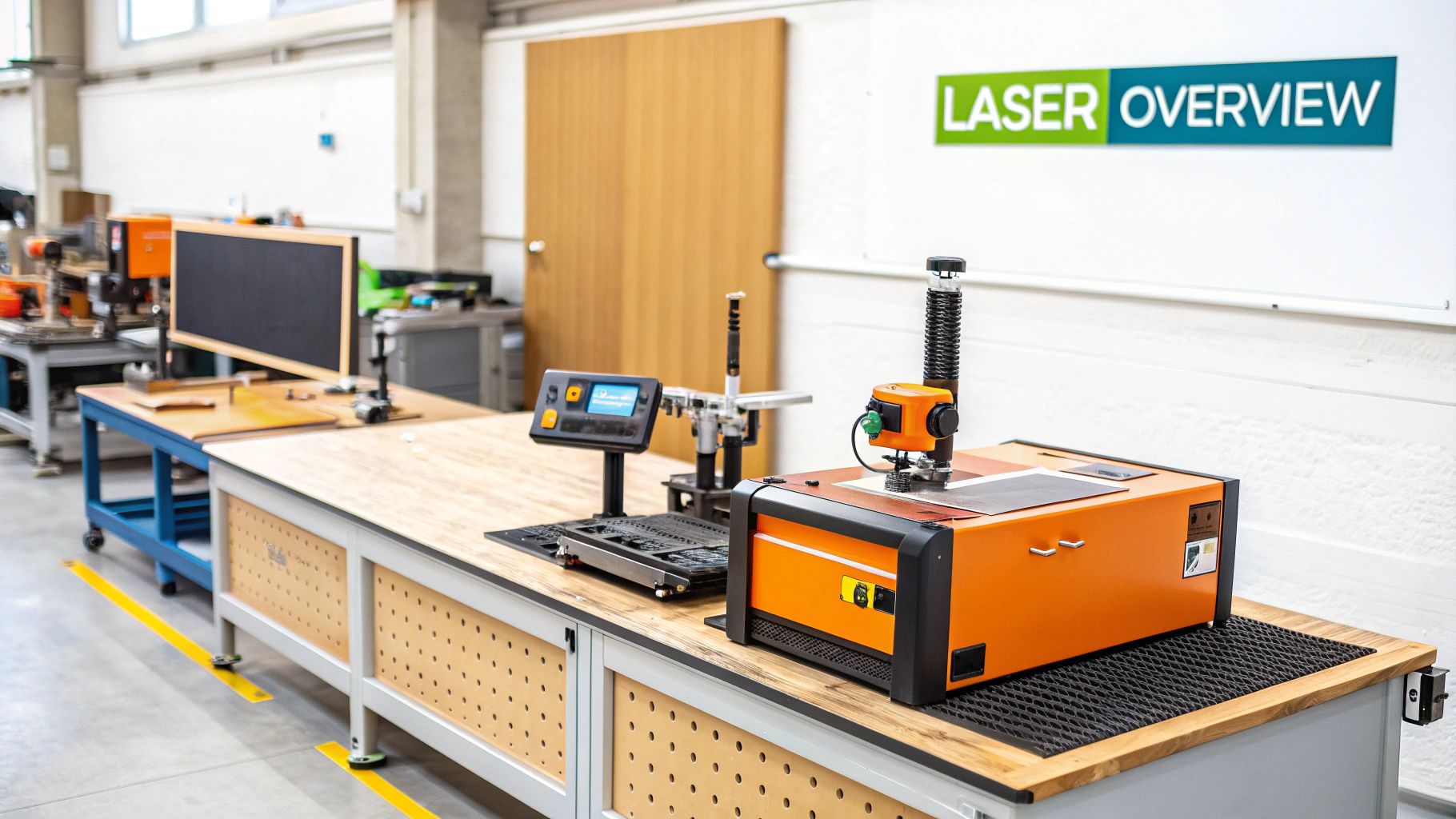

Precision in machine alignment is essential for optimal performance and a longer lifespan. This is even more important with today's complex, high-speed machinery. Laser alignment procedures have greatly improved, offering levels of accuracy and efficiency not possible before.
From Dial Indicators to Laser Beams: A Leap in Accuracy
Early machine alignment relied on dial indicators. These methods, while effective, were time-consuming and required skilled technicians. The process was also prone to human error, affecting the overall accuracy. This often meant longer downtime and recurring misalignment issues.
The introduction of laser technology in the 1960s changed everything. Optical alignment methods provided a significant improvement.
These early laser systems offered a more direct and accurate way to measure misalignment, reducing reliance on subjective interpretations. This resulted in better accuracy and faster alignment times. Ultimately, this meant improved machine performance, lower energy consumption, and a longer lifespan for equipment.
To further illustrate the evolution of these technologies, the table below provides a comparison across different eras:
Let's explore the progression of alignment technologies in more detail. The following table showcases key improvements throughout industrial history.
Evolution of Alignment Technologies
| Time Period | Technology | Key Features | Accuracy Level | Typical Application Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before 1960s | Dial Indicators | Mechanical measurement, relies on technician skill | Lower, prone to human error | Several hours |
| 1960s | Optical Alignment | Uses laser beams for measurement | Moderate improvement over dial indicators | 1-2 hours |
| 1980s | First Commercial Laser Alignment Systems (Prueftechnik OPTALIGN) | Electronic sensors and digital displays | Significantly higher accuracy | Less than 1 hour |
| Modern Day | Advanced Laser Alignment Systems | Software-driven, wireless communication, advanced features | Very high accuracy, automated reporting | Minutes |
The development of laser alignment tools has significantly enhanced machinery performance and longevity. For instance, proper alignment can lead to significant energy savings. One study found that aligning machines within tight tolerances could save up to $101,360 per year. For more information, check out this blog post: The Evolution of Shaft Alignment Technologies
Modern Advancements: Refining the Laser Alignment Procedure
The progress didn't stop there. Further developments in laser alignment technology continue to improve precision and usability. Modern systems include sophisticated software and hardware that simplify the alignment process, guiding technicians through each step and minimizing potential errors. This reduces the need for extensive specialized training, making precise alignment more accessible to a wider range of maintenance personnel.
The Impact of Precision: More Than Just Alignment
The advantages of accurate laser alignment go beyond ensuring machinery runs smoothly. Precise alignment is key to reducing wear and tear on components, lowering energy waste, and preventing unplanned downtime. This directly affects a company's bottom line, saving money on repairs, energy bills, and lost production. Furthermore, it contributes to a safer work environment by decreasing the risk of equipment malfunctions. The benefits are numerous and contribute significantly to the overall health and profitability of any operation that uses rotating machinery.
Choosing Your Arsenal: Essential Equipment That Delivers

A successful laser alignment procedure depends on the right tools and equipment. This involves more than just possessing a laser alignment system. It necessitates understanding the subtleties of different systems and their parts. This knowledge empowers you to make well-informed choices and optimize your laser alignment procedure for peak effectiveness.
Single vs. Dual-Laser Systems: Making the Right Choice
A key decision in laser alignment is selecting between single-laser and dual-laser systems. Single-laser systems are typically more budget-friendly and well-suited for simple alignments. However, they can be more time-intensive, demanding several measurements and computations.
Dual-laser systems, while often more expensive, provide superior speed and accuracy, especially for intricate machine setups. They measure both shafts concurrently, considerably shortening the overall alignment time. This benefit is particularly noticeable when working with large or hard-to-reach machinery.
Wireless Connectivity: Enhancing Your Alignment Process
Wireless functionality is becoming more prevalent in laser alignment systems. This feature simplifies data transfer and remote operation of the alignment procedure. While not a necessity in all cases, wireless capabilities can be extremely helpful in locations where physical access to the equipment is restricted or unsafe.
This eliminates the need for manual data entry and minimizes the chance of mistakes. For example, in tight spots or high-temperature zones, wireless systems offer a safer and more effective option compared to traditional wired configurations. You might be interested in: How to master...
Mounting Hardware: The Foundation of Accurate Alignment
The stability of the mounting hardware directly influences the precision of the laser alignment procedure. Durable and readily adjustable mounts are crucial for guaranteeing accurate measurements. Magnetic mounts are widely used due to their ease of use, yet their suitability hinges on the machinery's material and surface condition.
In demanding settings with excessive vibrations or uneven surfaces, more specialized mounting solutions may be required. These might include chain-type brackets or custom-made fixtures. Selecting appropriate mounting hardware can significantly improve the overall effectiveness and dependability of the alignment.
Software and Features: Choosing What Matters
Modern laser alignment systems frequently include advanced software. While some features are essential, others might be less useful for everyday tasks. Crucial features include thermal growth compensation, which modifies alignment targets based on temperature fluctuations, and reporting functions, which create detailed alignment reports automatically.
Less vital features, though possibly helpful in specific situations, might increase complexity and expense without yielding major advantages for most alignment jobs. Carefully assessing your requirements and selecting a system with the ideal combination of software and features is essential for maximizing your investment.
To help you choose the right laser alignment system, we've compiled a comparison table highlighting the key features, applications, and price ranges of different system types:
Laser Alignment System Comparison: A detailed comparison of different laser alignment systems based on capabilities, applications, and price ranges to help readers select the right equipment for their needs.
| System Type | Key Features | Accuracy | Best Applications | Price Range | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Beam Laser | Simple, cost-effective | Moderate | Basic alignment tasks, small machines | $1,000 - $5,000 | Time-consuming, less accurate for complex alignments |
| Dual-Beam Laser | Simultaneous measurement, faster alignment | High | Complex alignments, large machines | $5,000 - $15,000 | Higher initial cost |
| Roll Alignment System | Measures roll parallelism and perpendicularity | Very High | Paper mills, printing presses, converting machines | $10,000 - $30,000 | Specialized application |
| Bore Alignment System | Aligns bores and bearings | High | Engines, pumps, compressors | $3,000 - $10,000 | Requires specific fixtures |
This table provides a general overview and specific prices and features may vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
As shown in the table, different laser alignment systems cater to various needs and budgets. Choosing the right system depends on the complexity of the alignment tasks, required accuracy, and budget constraints.
Building Your Ideal Toolkit
In the end, choosing the correct equipment involves weighing budget constraints against the particular requirements of your alignment jobs. Prioritizing important features like dual-laser capability, reliable mounting hardware, and essential software features will result in a more productive and precise laser alignment process. Furthermore, proper instruction on operating the selected system ensures your investment translates into real-world enhancements in machine reliability and performance.
The Perfect Laser Alignment Procedure: A Master Class

Having the right equipment is essential for laser alignment. However, understanding the proper procedure is crucial for achieving optimal results. This section outlines a proven sequence used by top maintenance teams to achieve precise and efficient alignment, minimizing downtime and maximizing the lifespan of your machinery.
Pre-Alignment Preparations: The Foundation for Success
Many overlook the importance of pre-alignment checks. These steps are vital for accurate measurements and error prevention. This phase involves cleaning the machine shafts and mounting surfaces. Removing debris ensures a solid base and prevents skewed readings. Also, inspect for loose components, worn bearings, or damaged couplings. Addressing these beforehand ensures a stable alignment.
Mastering Mounting Techniques: Securing Accurate Measurements
Proper mounting of the laser alignment system is critical. Incorrect mounting can lead to significant errors and flawed corrections. Mounting hardware should be firmly attached to the shafts using appropriate methods like magnetic mounts, chain brackets, or custom fixtures. The key is stability throughout the procedure, guaranteeing consistent data capture.
Interpreting the Data: Uncovering Hidden Issues
Correctly interpreting data after measurements is essential. This involves understanding misalignment types like angular, offset, and combined misalignment. Modern laser alignment systems and software can help visualize misalignment values and guide the correction process. However, identifying the root cause is crucial. For example, soft foot, where a machine foot doesn't fully contact the baseplate, can severely impact alignment. Correcting this before other adjustments is a prime example of effective data interpretation.
The Sequence of Corrections: Order Matters
Correcting misalignment requires a systematic approach. The order of adjustments is vital. Typically, vertical alignment is addressed first, followed by horizontal alignment. This structured approach prevents compounding errors. Think of building a house: the foundation comes before the roof. Similarly, a structured approach is essential for lasting alignment.
Thermal Growth Considerations: Aligning for Real-World Conditions
Machines operate under varying temperatures, impacting alignment. Thermal growth, the expansion or contraction due to temperature changes, must be considered. Modern systems offer thermal growth compensation, adjusting alignment targets based on the expected operating temperature. This ensures alignment during operation, minimizing wear and maximizing performance.
Machine-Specific Techniques: Tailoring the Procedure
While general laser alignment principles remain consistent, machine-specific techniques may be necessary. Aligning a large turbine differs from aligning a small pump. This might involve specialized hardware, specific measurements, or unique adjustments. Understanding these nuances distinguishes a competent technician from a true alignment expert.
By following this procedure, incorporating pre-alignment checks, precise mounting, accurate data interpretation, a systematic correction sequence, and considering thermal growth, you can achieve perfect laser alignment. This comprehensive approach improves machine reliability and performance while minimizing downtime and extending equipment life.
Troubleshooting Like a Pro: Solving Alignment Challenges
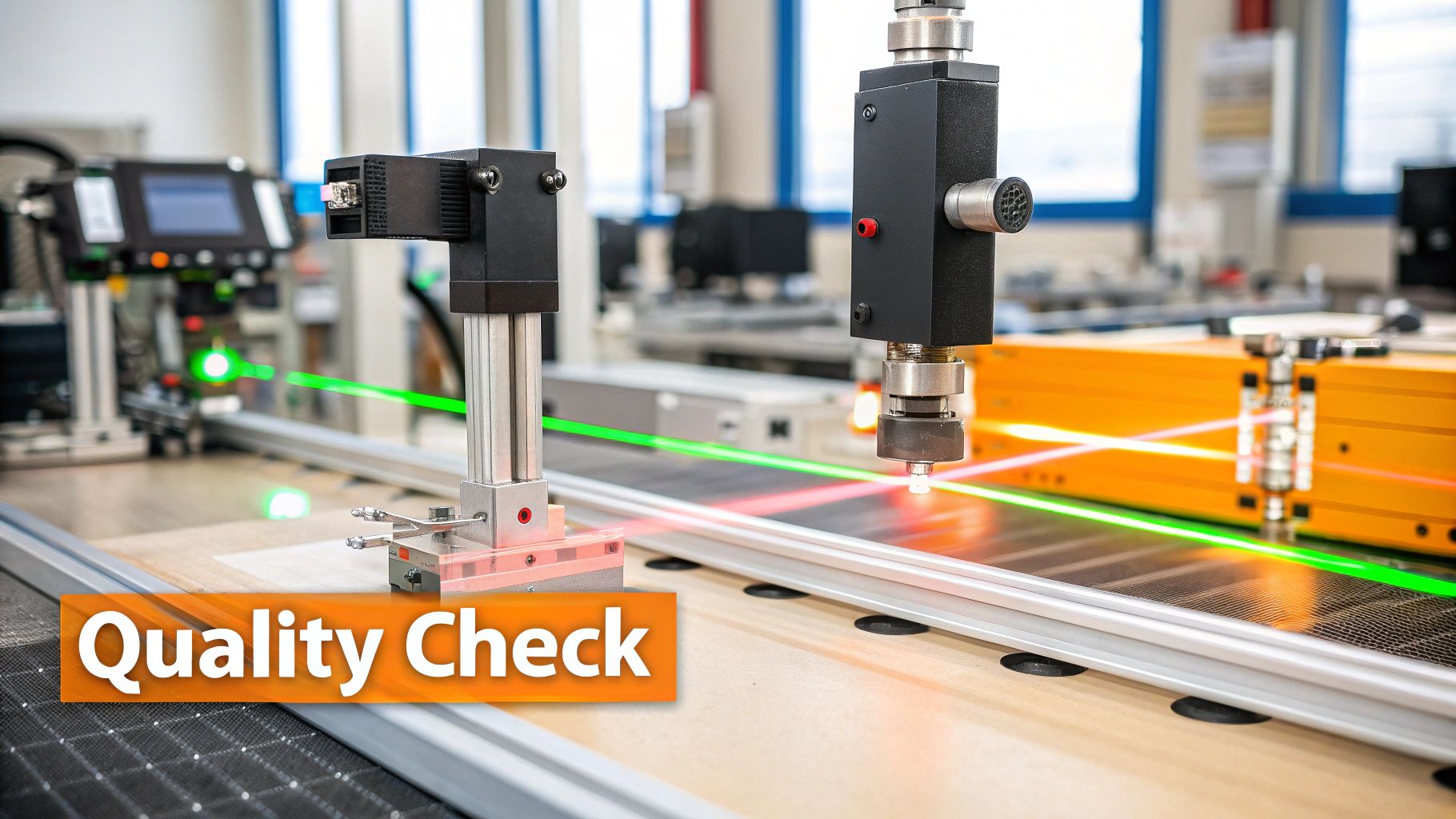
Even with a flawless laser alignment procedure, you might still encounter some bumps in the road. This section tackles common obstacles during laser alignment and offers practical solutions for overcoming them efficiently. These troubleshooting techniques will save you precious time and boost your alignment success rate.
Beam Interruptions: Maintaining a Clear Line of Sight
A frequent issue is beam interruption during the alignment process. This happens when something obstructs the path between the laser transmitter and receiver.
For example, a coupling guard or a pipe could block the laser beam. This prevents accurate measurements. The solution is simple: identify and remove the obstruction.
Alternatively, reposition the laser alignment units. This helps establish a clear line of sight. Often, a minor tweak to the setup can resolve the issue.
Soft Foot: Ensuring a Stable Foundation
Soft foot refers to a condition where a machine's foot doesn't make complete contact with its baseplate. This instability can significantly impact alignment accuracy.
Soft foot can show up as a gap between the foot and baseplate, or as excessive strain on the mounting bolts. Identifying and fixing soft foot is crucial for a stable and precise alignment.
This usually involves shimming the foot or machining the baseplate to guarantee proper contact.
Bolt-Bound Conditions: Freeing Up Movement
Bolt-bound conditions arise when mounting bolts are over-tightened. This restricts the machine's movement during the alignment procedure.
Over-tightening makes adjustments difficult or even impossible. The solution is to loosen the bolts slightly. Loosen them just enough to allow free movement without sacrificing stability.
This enables the required adjustments during the laser alignment. Remember to re-tighten the bolts to the correct torque specification after achieving proper alignment.
Environmental Factors: Minimizing External Influences
Environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and vibrations, can impact alignment accuracy. Temperature changes can cause thermal growth in machinery, altering alignment after the procedure.
Vibrations can also disrupt laser readings. This leads to inaccurate measurements. To address these factors, incorporate thermal growth compensation features in your alignment system.
Additionally, perform alignments in a stable environment. Planning ahead is key to minimizing these external influences.
Data Interpretation: Understanding the Numbers
Misinterpreting alignment data can result in incorrect adjustments and wasted time. Understanding the different misalignment types—angular, offset, and combined—is crucial.
For further insights, check out our guide on How to master.... Properly using alignment software is also essential.
The software can visualize the misalignment and guide the correction process. However, it's the technician's understanding that ultimately leads to accurate adjustments.
Building a Troubleshooting Mindset
A proactive troubleshooting approach begins with careful observation. Understand the potential challenges before they occur.
This includes recognizing early warning signs. Intermittent beam interruptions or unusual readings are good examples. By anticipating issues and implementing preventative measures, you can improve the alignment process.
This proactive mindset, combined with the troubleshooting techniques discussed above, will empower you to handle even the most complex alignment situations. The result is improved machine performance, lower maintenance costs, and increased operational efficiency.
Beyond Maintenance: The Business Impact of Precision Alignment
Laser alignment isn't just a routine maintenance task; it's a strategic decision that can significantly impact your bottom line. Accurately aligning machinery with a laser system leads to substantial cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Let's explore the tangible business advantages and how maintenance teams can showcase the return on investment (ROI) of this critical process.
Quantifying the Financial Returns of Laser Alignment
Proper alignment minimizes wear and tear, extending the lifespan of your equipment. This directly translates to reduced capital expenditures on replacements and major overhauls. Moreover, precise alignment optimizes energy consumption. Misaligned components create friction, resulting in higher energy demands. Using laser alignment, businesses can significantly reduce their energy bills, directly impacting profitability.
For example, a chemical plant in Derbyshire saw a remarkable improvement in pump reliability after implementing a laser alignment program. Their mean time between failures (MTBF) increased from 10 months to over 46 months, leading to annual maintenance savings of more than $157,000. This highlights the considerable cost-effectiveness and efficiency gains achievable through accurate alignment. Find more detailed statistics here: Shaft Alignment Instructions
Demonstrating Alignment ROI to Management
When communicating the value of laser alignment to management, emphasize Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) aligned with business goals. Track reductions in maintenance costs, downtime, and energy use. Quantify these improvements in financial terms to demonstrate the direct positive impact on profitability.
Compare maintenance expenses before and after implementing a laser alignment program. Analyze downtime records to illustrate the reduction in lost production time due to equipment malfunctions. These metrics provide concrete evidence of the financial advantages. More information can be found here: Laser Alignment Resources
Elevating Maintenance From Cost Center to Profit Driver
Maintenance teams often face challenges securing necessary resources. By showcasing the substantial ROI of laser alignment, these departments can justify investments in advanced tools and training. Demonstrating tangible results elevates the perception of maintenance from a cost center to a key contributor to the organization's financial success.
Building a Culture of Alignment Excellence
Successfully implementing laser alignment involves more than simply acquiring the technology. It requires fostering a culture of precision and continuous improvement within the maintenance team. This includes establishing standardized procedures, providing ongoing training, and maintaining thorough documentation to ensure consistent, high-quality results. By prioritizing alignment excellence, businesses can unlock substantial benefits and transform their maintenance operations into a source of competitive advantage.
Building a World-Class Alignment Program That Sticks
Moving beyond individual laser alignment procedures, this section explores how leading organizations build sustainable alignment programs that elevate their entire maintenance approach. These programs go beyond simply using the technology; they integrate best practices, training, and documentation to ensure long-term success.
Standardizing Procedures Without Stifling Innovation
Successful alignment programs often begin with standardized laser alignment procedures. This provides a baseline for quality and consistency across all alignment tasks. A well-defined procedure outlines pre-alignment checks, mounting techniques, measurement steps, and correction methods.
This ensures everyone follows the same process, minimizing errors and improving repeatability. However, standardization shouldn't stifle innovation. Allow room for technicians to adapt the procedure to specific machine types or unique situations.
Encourage feedback and continuous improvement to refine the process over time. This balance between standardization and flexibility ensures a robust yet adaptable alignment program.
Training: Creating Alignment Experts
Effective training is the cornerstone of any successful program. Don't just train operators on how to use the equipment; cultivate true alignment experts. Comprehensive training programs should cover the fundamentals of alignment theory, proper use of laser alignment systems, and advanced troubleshooting techniques.
Consider incorporating hands-on workshops and certification programs to reinforce practical skills. This approach develops a deeper understanding of alignment principles, enabling technicians to handle complex situations and contribute to continuous program improvement. Investing in training yields significant returns in improved accuracy, reduced downtime, and greater overall effectiveness.
Integrating Alignment Into Existing Workflows
Introducing new procedures requires careful integration into existing maintenance workflows. Instead of disrupting established routines, look for seamless ways to incorporate alignment into current schedules. This might involve adding pre-alignment checks to routine inspections or incorporating alignment tasks into preventative maintenance plans.
A phased implementation can also ease the transition. Start with a pilot program on a specific group of machines and gradually expand to other areas as the team gains experience. This minimizes disruptions and allows for adjustments based on real-world feedback during the initial rollout.
Documentation: Capturing Critical Knowledge
Proper documentation is often overlooked, but it's essential for maintaining a world-class alignment program. Documenting standardized procedures, training materials, and alignment results creates a valuable knowledge base. This helps retain expertise and ensures consistency over time.
This is particularly important for preserving the knowledge of experienced technicians before they retire. Their insights and practical tips can be invaluable for training new team members. A robust documentation system also simplifies troubleshooting and helps identify trends or recurring problems.
Managing Change in Maintenance Environments
Implementing a new alignment program often faces resistance. Successfully navigating this change requires a thoughtful approach. Clearly communicate the benefits of the new program, emphasizing how it will improve technicians' daily work and contribute to overall plant performance.
Involve the maintenance team in the implementation process, seeking their input and addressing their concerns. This builds support and ensures a smoother transition. Recognize and reward early adopters to create a culture of continuous improvement. By addressing these factors, you improve the chances of building a program that endures.
The Future of Laser Alignment: Tools and Trends You Need To Know
Laser alignment procedures are essential for maintaining machinery efficiency and extending its operational life. But technology is always evolving. This section explores emerging tools and trends shaping the future of laser alignment, helping you stay ahead of the curve and adapt your maintenance strategies.
Continuous Monitoring: Challenging The Status Quo
Traditional laser alignment relies on periodic checks. However, continuous monitoring systems are changing the game. These systems use sensors to track machine alignment in real-time, constantly providing feedback on any deviations. This allows for immediate corrective action, stopping small misalignments from becoming major issues.
This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends equipment lifespan. It represents a significant shift towards predictive maintenance, going beyond scheduled checks to address issues as they develop.
Augmented Reality: Enhancing Precision and Accessibility
Augmented reality (AR) is transforming laser alignment procedures. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, providing technicians with a visual guide during alignment. This improves precision and reduces human error.
For example, AR can project the ideal alignment onto the machine, showing the technician exactly how to make adjustments. This makes laser alignment more accessible, allowing less experienced personnel to perform complex tasks. AR also has the potential to revolutionize training and on-site support by making expert guidance available remotely.
Cloud Connectivity and Data Analysis: Unlocking Predictive Insights
Cloud platforms are increasingly integrated with laser alignment systems. This connectivity allows for seamless data transfer and storage, enabling powerful analysis and reporting. Maintenance teams can access historical alignment data, identify trends, and predict potential problems.
This shift toward data-driven maintenance empowers organizations to optimize maintenance strategies, minimize downtime, and improve overall equipment effectiveness. Tracking alignment data might reveal that a specific machine tends to misalign faster after certain operating conditions, allowing for targeted preventative maintenance.
Industry 4.0 and Laser Alignment: Separating Hype From Reality
Industry 4.0, with its focus on automation and data exchange, holds significant potential for laser alignment. It's important, however, to distinguish real advancements from passing fads.
While some Industry 4.0 concepts, like remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance through cloud connectivity, offer real benefits, others may not be practical or cost-effective for every situation. Focusing on solutions that address specific challenges and integrate with existing workflows will be crucial for maximizing the value of Industry 4.0 in laser alignment. For instance, automated alignment correction systems, while promising, may be overly complex and expensive for many applications in their current stage of development.
Staying informed about these developments is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in industrial maintenance. By adopting these tools and trends, you can improve your laser alignment procedures, optimize maintenance strategies, and ensure long-term equipment reliability. Ready to improve your laser alignment procedures? Laser Insights China provides information and resources to help you stay at the forefront of this evolving field. From in-depth technical guides to expert interviews, we cover the latest trends and technologies impacting the laser industry. Visit us today and discover how we can help you achieve alignment excellence.

